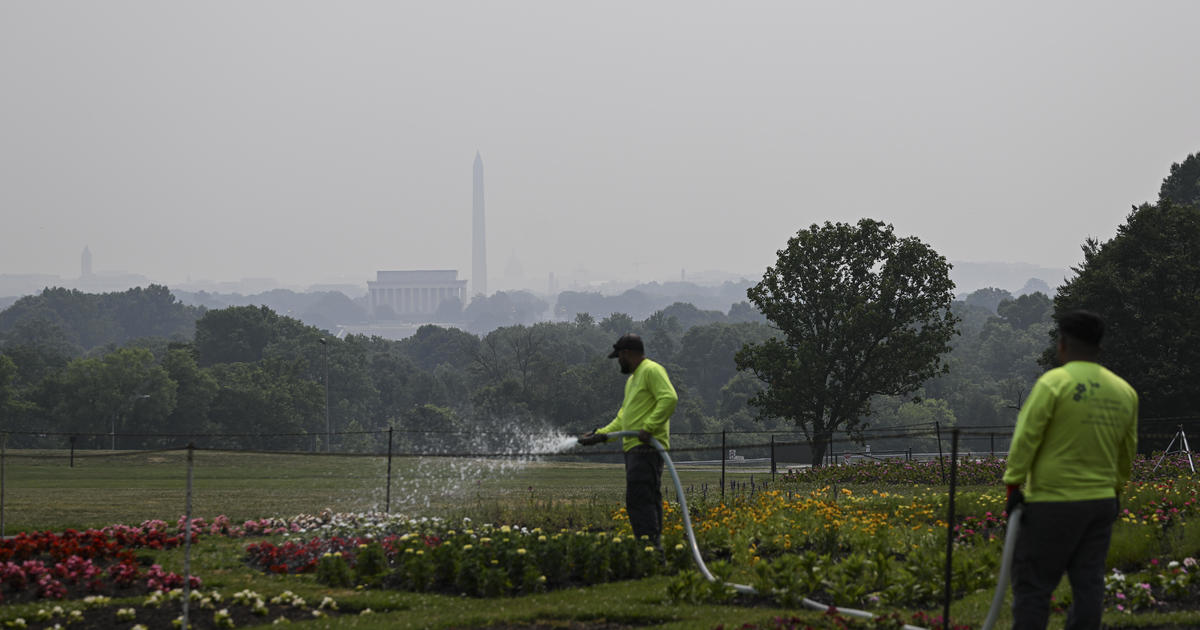
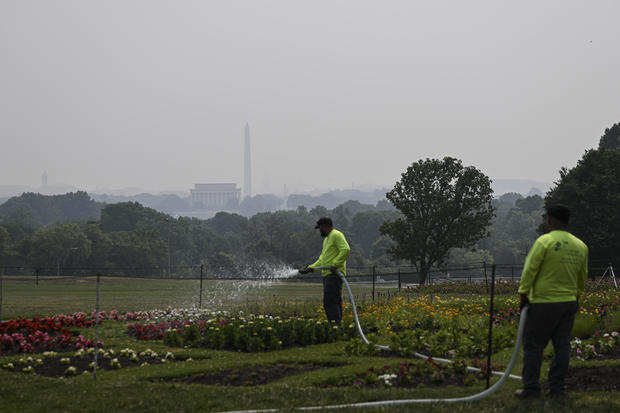
With the smoke from burning Canadian forests enveloping the U.S. Northeast, major cities fell silent this week. Public schools canceled outdoor activities, companies sent workers home, performances were postponed, libraries shut their doors and professional baseball games were canceled.
Such disruptions in ordinary urban life illustrates the wide-ranging economic toll of climate change, which experts say is making wildfires more intense and contributing to air pollution.
“It’s gray and the sun looked orange in the sky this morning, like Star Wars or something,” Paul Billings, national vice president for public policy at the American Lung Association, told CBS MoneyWatch from Washington, D.C.
“It’s really early in the season, we’re still in the spring, and we’re seeing these wildfires in Canada and the U.S. that are impacting air quality across the eastern United States. In New England, across the mid-Atlantic and into Minnesota, we’re seeing elevated levels of particulate matter or soot,” he added.
These tiny particles are especially dangerous for people with heart disease, asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but they carry risks for everyone, including risks of asthma attacks, heart attack, stroke or early death.
“Some people need to take their medication more — others end up in the emergency room,” Billings said.
Because the kind of particles found iin smoke are so small, they get past the body’s natural defenses, such as mucus membranes in the nose and throat as well as the body’s coughing mechanism.
“They penetrate deep in the lungs and where you have oxygen exchange systems,” Billings said. “These particles actually get into your blood and create a wide range of poor health outcomes, including stroke, heart attacks and different kinds of cancer.”
Forest fires aren’t the only source of particulate matter — diesel trucks and coal-fired power have historically contributed the lion’s share of air pollution. But wildfires are a growing factor. The increased frequency of wildfires in a hotter, drier climate has reversed some of the improvements in air quality since the 1970 Clean Air Act, the American Lung Association noted in an April report.
“Staggering” costs
The earth’s warming climate is contributing to the problem, with temperatures in Canada unseasonably high this year. Lytton, British Columbia — typically a temperate town — hit a record high of 121 degrees last week, tying California’s Death Valley. Hot, dry weather makes it more likely that a forest will catch fire and burn longer. Already, Canada’s wildfire season is on track to be the most destructive in the country’s history.
Globally, air pollution kills more than 3 million people a year, according to the World Health Association. In dollar terms, the costs are vast and reflected in increased hospitalizations, missed work and school days, and lower worker productivity.
“The costs are staggering,” Billings said
Air pollution adds $2,500 a year to a typical American’s medical bills, a recent study from the Natural Resources Defense Council found. Across the U.S., smoke, factory output and car exhaust cost the economy $800 billion a year, or about 3% of the nation’s total economic output, the NRDC found.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, high levels of air pollution also reduce earnings by making it harder and more unpleasant to work, adding a significant drag on the economy. Outdoor workers, such as delivery people, and landscapers and teachers are most affected, but office workers aren’t necessarily safe. Even indoor air pollution spikes to three or four times safe levels during a wildfire event, studies have found.
$125 billion in lost pay
Researchers at Stanford who mapped wildfire plumes across the U.S. found that a single day of smoke exposure lowers a person’s quarterly earnings by 0.1%, according to a recent working paper published by the National Bureau of Economic Research. Across the U.S. as a whole, workers lost $125 billion a year due to wildfire smoke, the paper found — about 2% of all labor income.
Aside from smoke, hotter air also increases production of ozone, a major component of smog and a lung irritant. “Some researchers have likened it to sunburn on the lungs — your cells get irritated and weep,” Billings said.
Celal Gunes/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images
As with other kinds of pollution, the effects of ozone, smog and smoke aren’t evenly distributed, with low-income people and people of color more likely to be exposed, according to the ALA.
Businesses and governments can take some steps, like improving indoor filtration, not forcing workers to go outside and alerting issuing public service alerts about air quality. But reducing the toll of air pollution long-term means widespread electrification, Billings said. That would reduce emissions from transportation and factories.
“I think too often, people look at these as anomalous weather events,” he said. “This is not some happenstance of a fire. It’s early June. There have always been fires, but the big driver that is creating these hot, dry conditions that are creating the opportunities for these fires is climate change.”